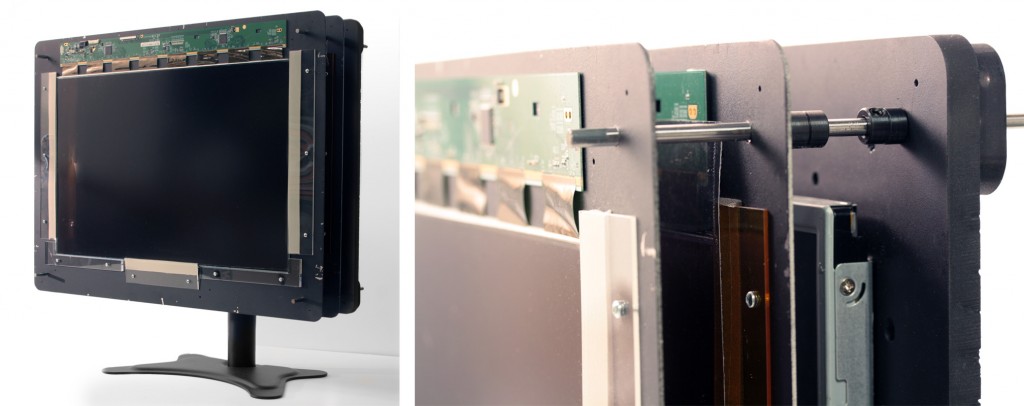
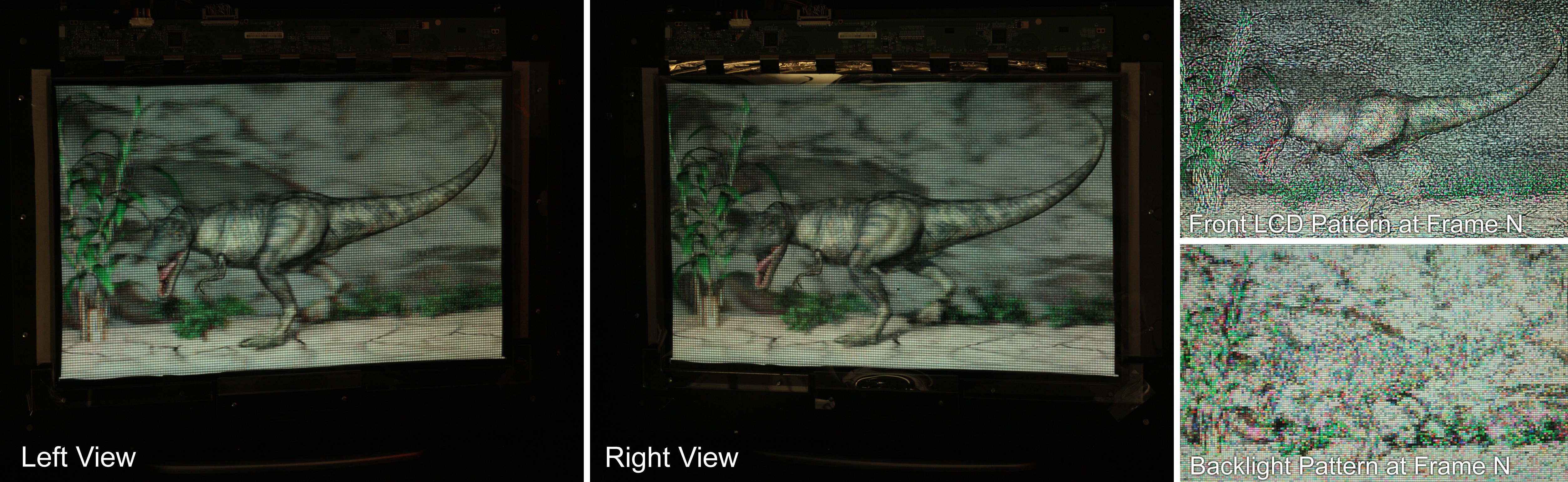
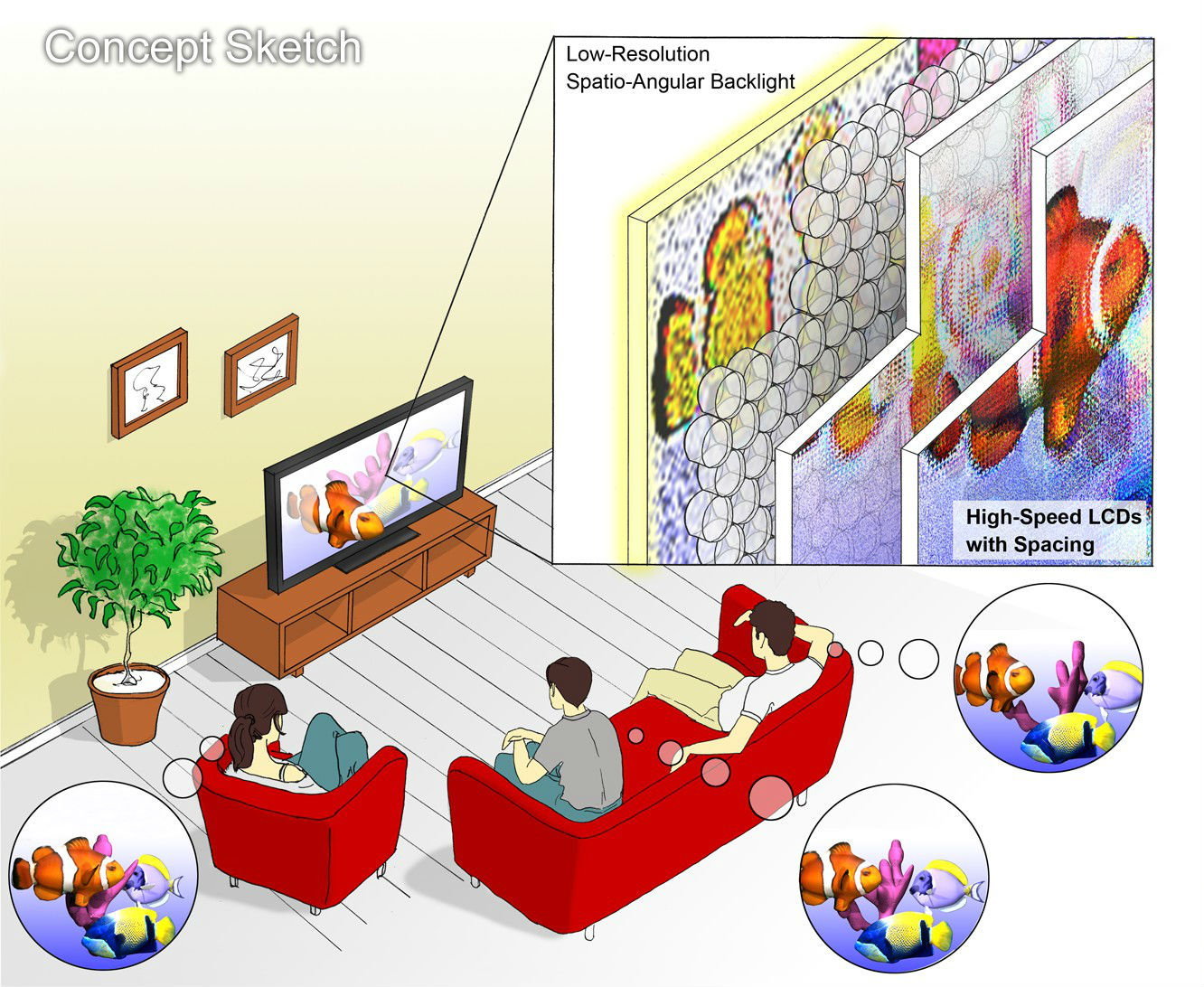
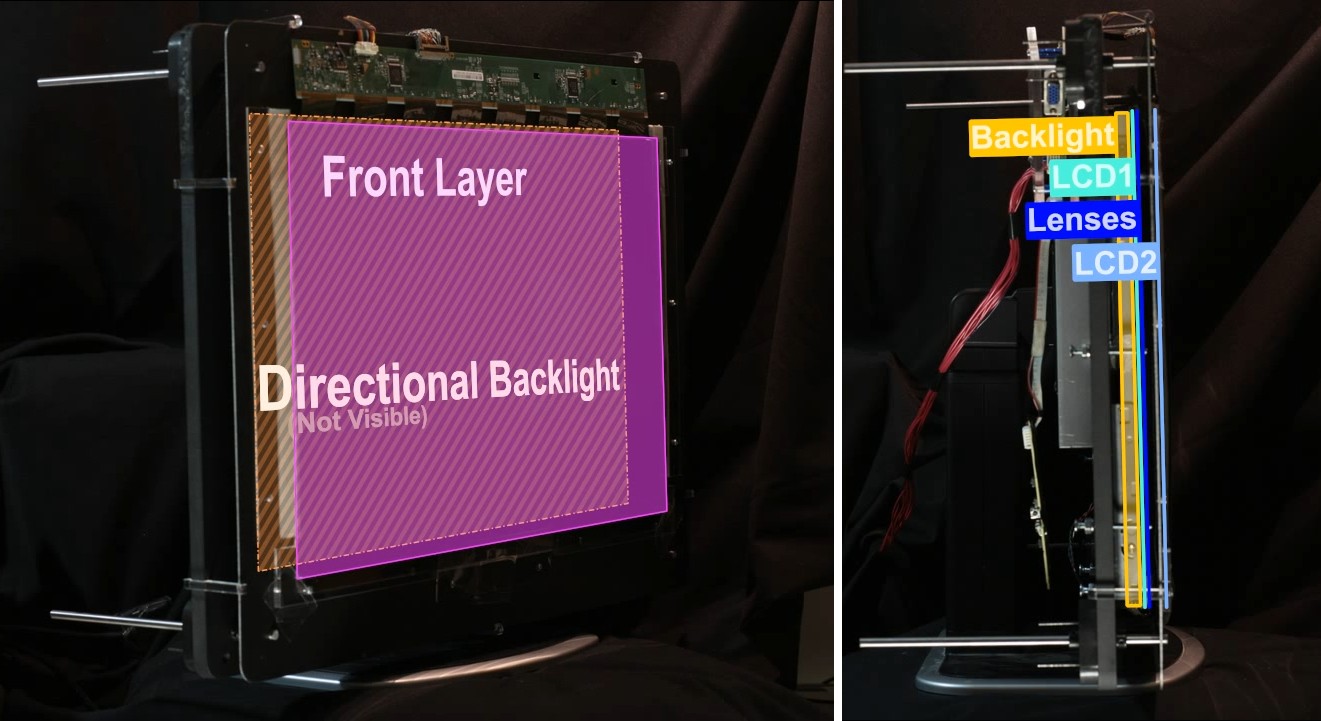
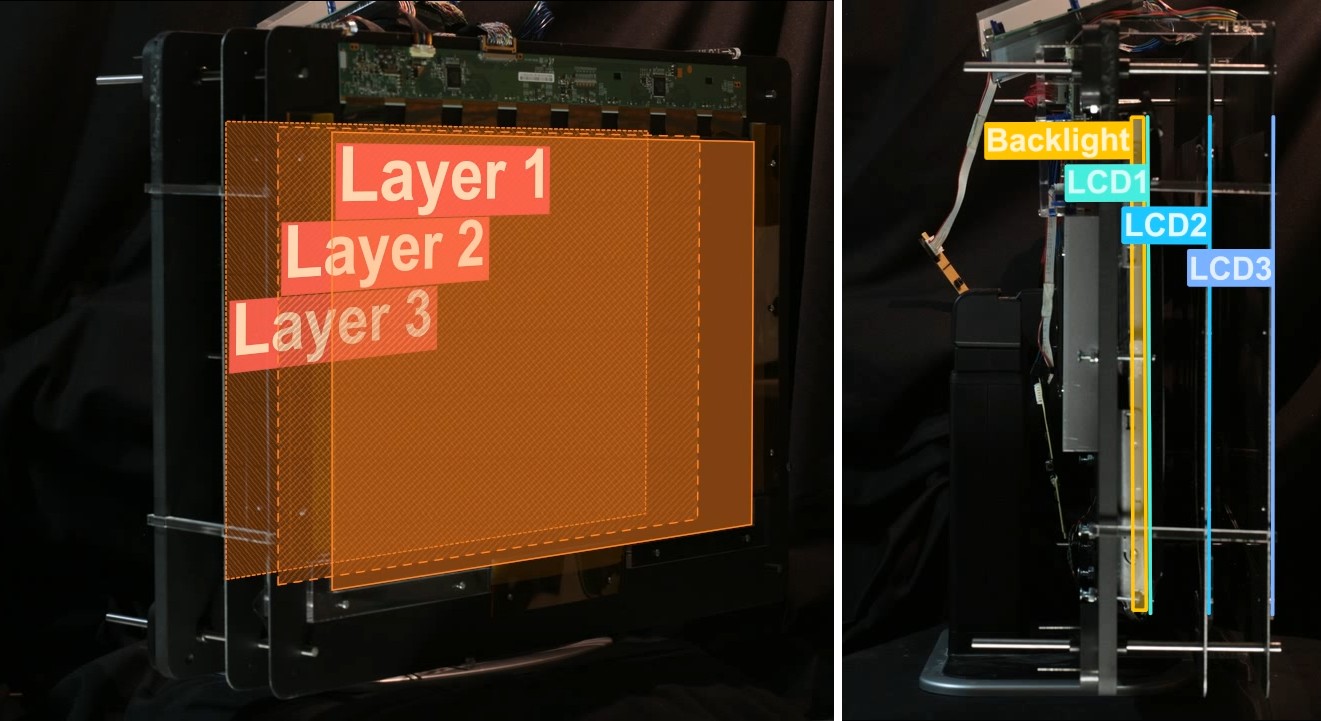
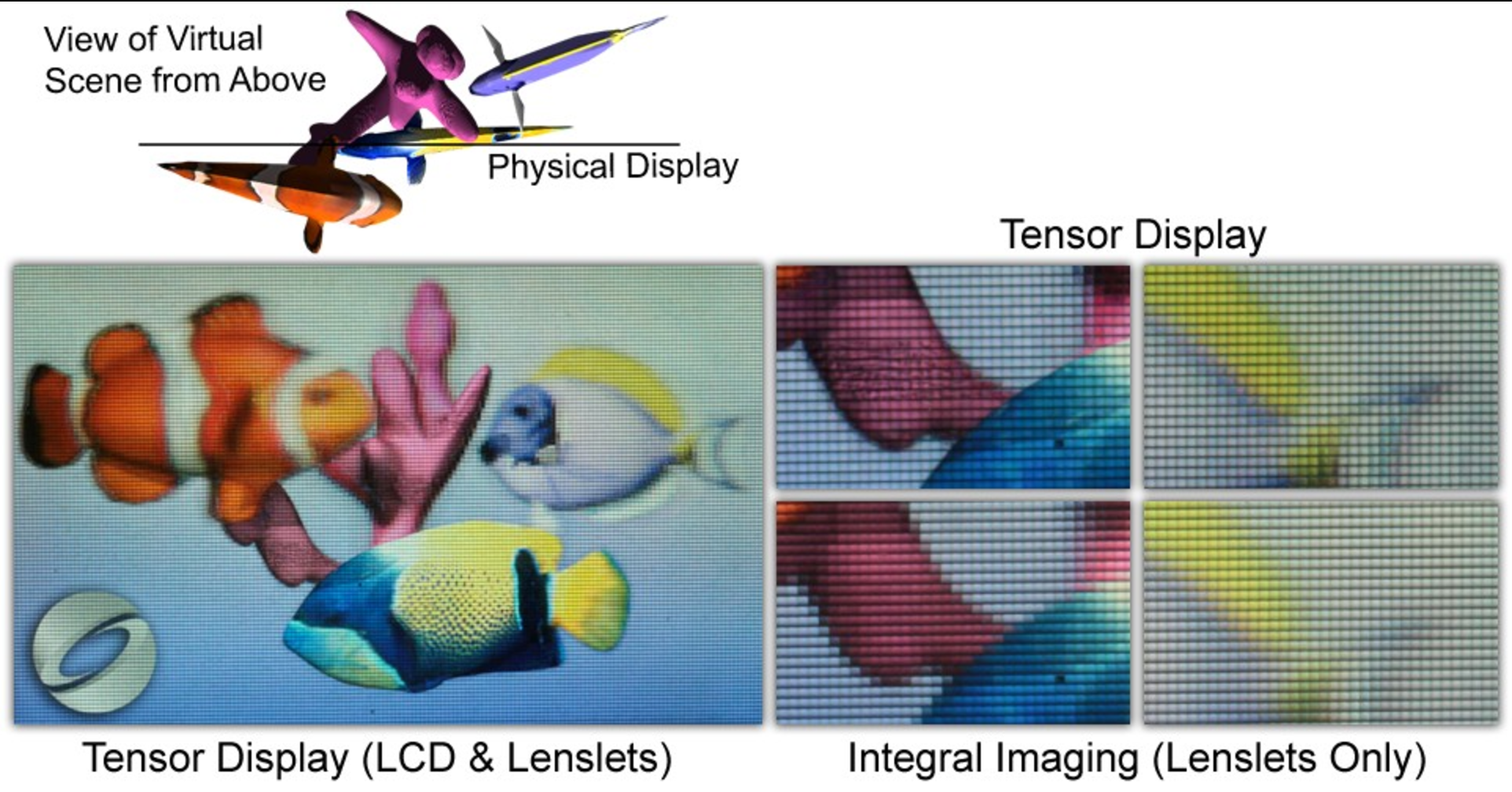
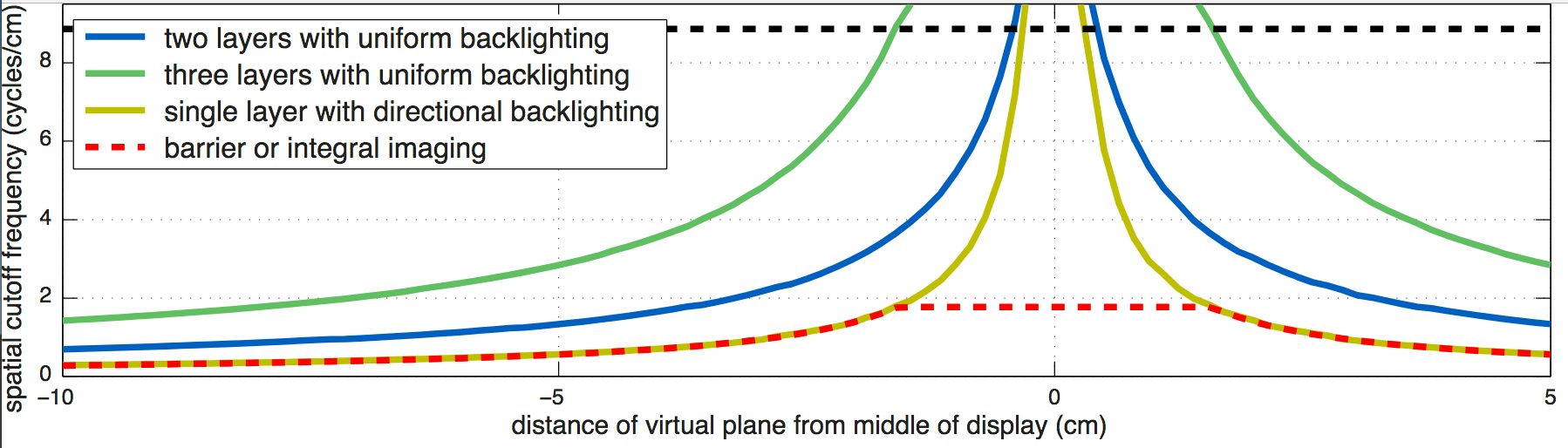
Wide field of view glasses-free 3D display using tensor displays. (Left) We introduce a new family of light field displays, dubbed tensor displays, comprised of stacks of light-attenuating layers (e.g., multilayer LCDs). Rapid temporal modulation of the layers is exploited, in concert with directional backlighting, to allow large separations between viewers. (Right) Photographs showing one of our multiview display prototypes (Fig. 2, right) from two different perspectives. Tensor displays support smooth motion parallax and binocular disparity at a high resolution for a large depth of field over a wide range of viewpoints.
ABSTRACT
We introduce tensor displays: a family of compressive light field displays comprising all architectures employing a stack of time-multiplexed, light-attenuating layers illuminated by uniform or directional backlighting (i.e., any low-resolution light field emitter). We show that the light field emitted by an N-layer, M-frame tensor display can be represented by an Nth-order, rank-M tensor. Using this representation we introduce a unified optimization framework, based on nonnegative tensor factorization (NTF), encompassing all tensor display architectures. This framework is the first to allow joint multilayer, multiframe light field decompositions, significantly reducing artifacts observed with prior multilayer-only and multiframe-only decompositions; it is also the first optimization method for designs combining multiple layers with directional backlighting. We verify the benefits and limitations of tensor displays by constructing a reconfigurable prototype using modified LCD panels and a custom integral imaging backlight. Our efficient, GPU-based NTF implementation enables interactive applications. Through simulations and experiments we show that tensor displays reveal practical architectures with greater depths of field, wider fields of view, and thinner form factors, compared to prior automultiscopic displays.