Additional Information
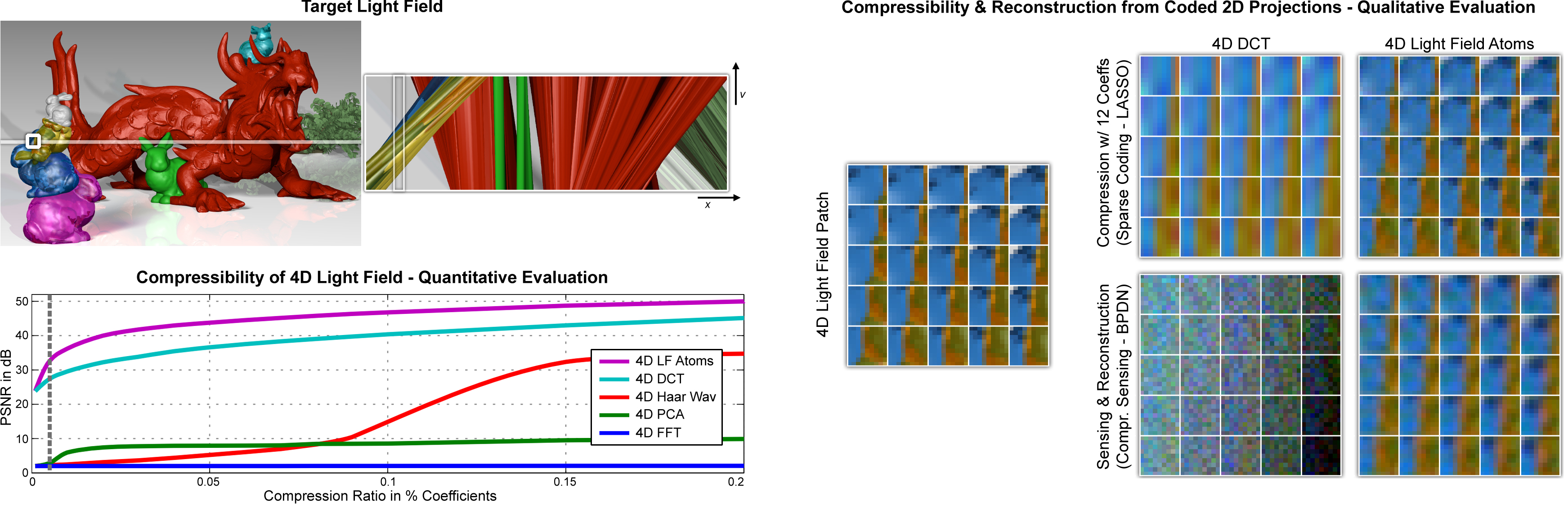
Compressibility of a 4D light field in various high-dimensional bases. As compared to popular basis representations, the proposed light field atoms provide better compression quality for natural light fields (bottom left). Edges and junctions are faithfully captured (right); for the purpose of 4D light field reconstruction from a single coded 2D projection, the proposed dictionaries combined with sparse coding techniques perform best in this experiment (right).
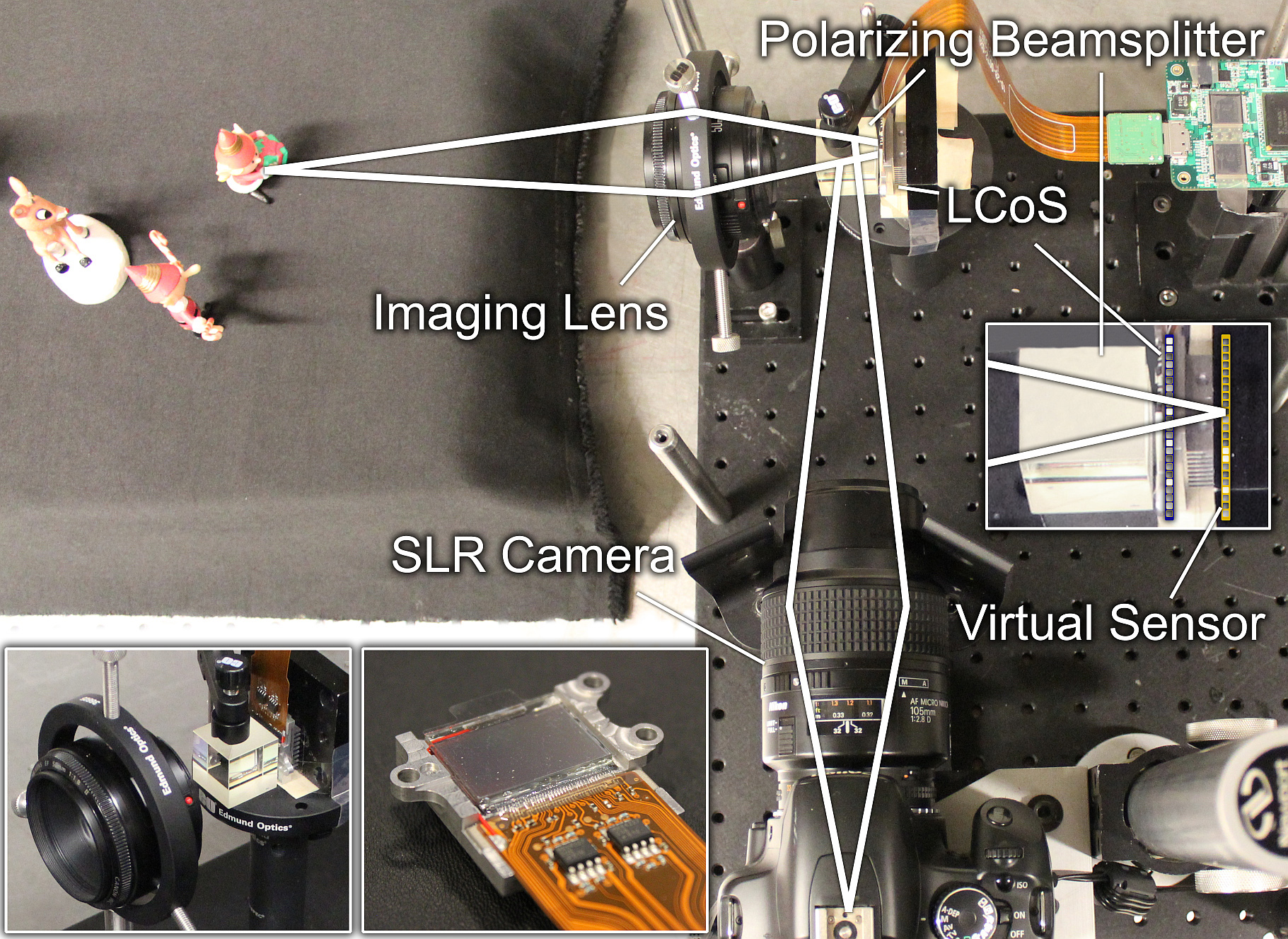
Prototype light field camera. We implement an optical relay system that emulates a spatial light modulator (SLM) being mounted at a slight offset in front of the sensor (right inset). We employ a reflective LCoS as the SLM (lower left insets).
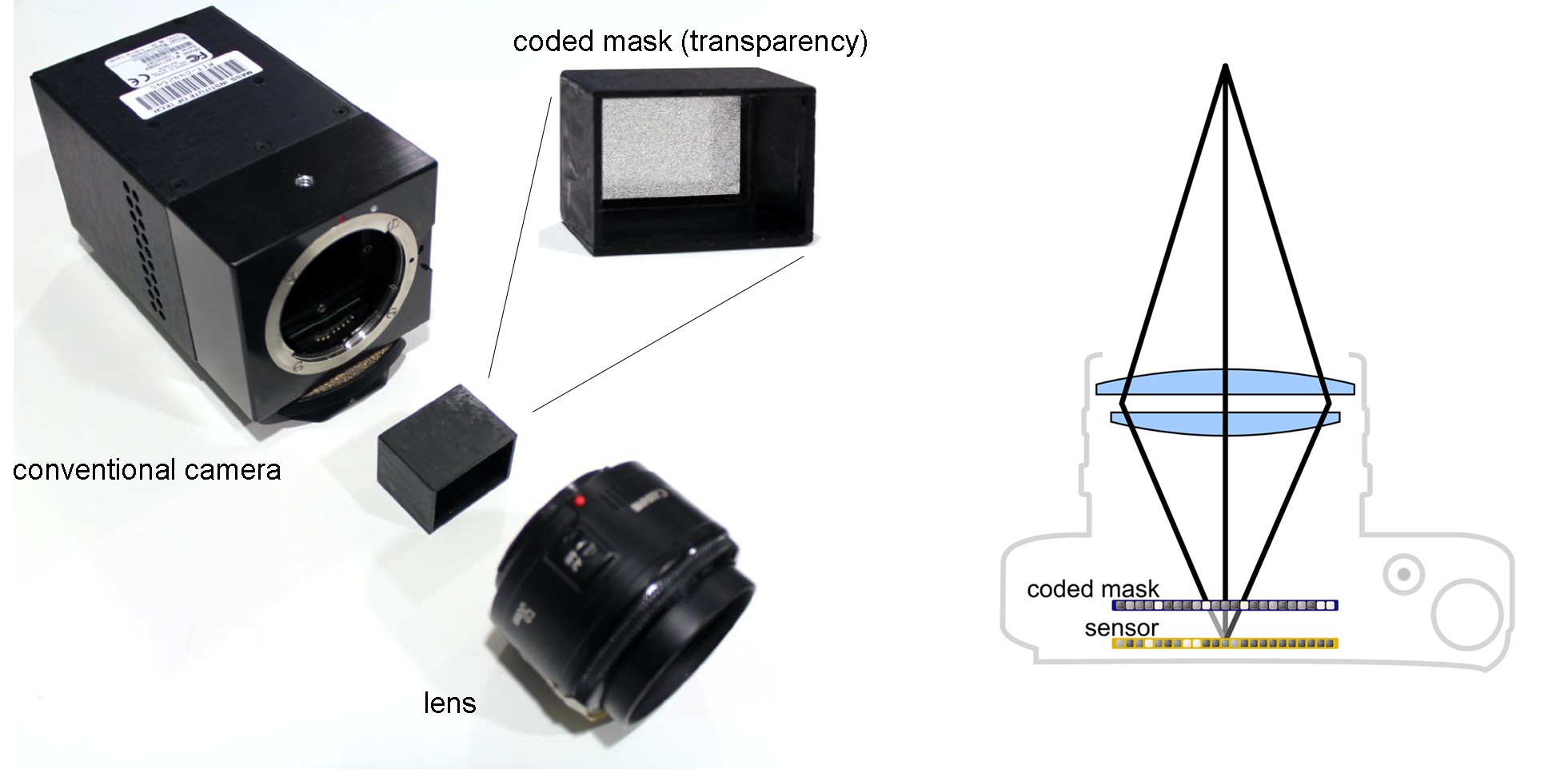
Second prototype light field camera. A conventional camera can also be retrofitted with a simple transparency mask to facilitate compressive light field photography (left). As shown on the right, the mask blocks some of the light rays inside the camera and therefore codes the captured image. This optical design combined with compressive computational processing could be easily integrated into consumer products.
Visualization of light field atoms captured in an overcomple dictionary. Light field atoms are the essential building blocks of natural light fields – most light fields can be represented by the weighted sum of very few atoms. We show that light field atoms are crucial for robust light field reconstruction from coded projections and useful for many other applications, such as 4D light field compression and denoising.
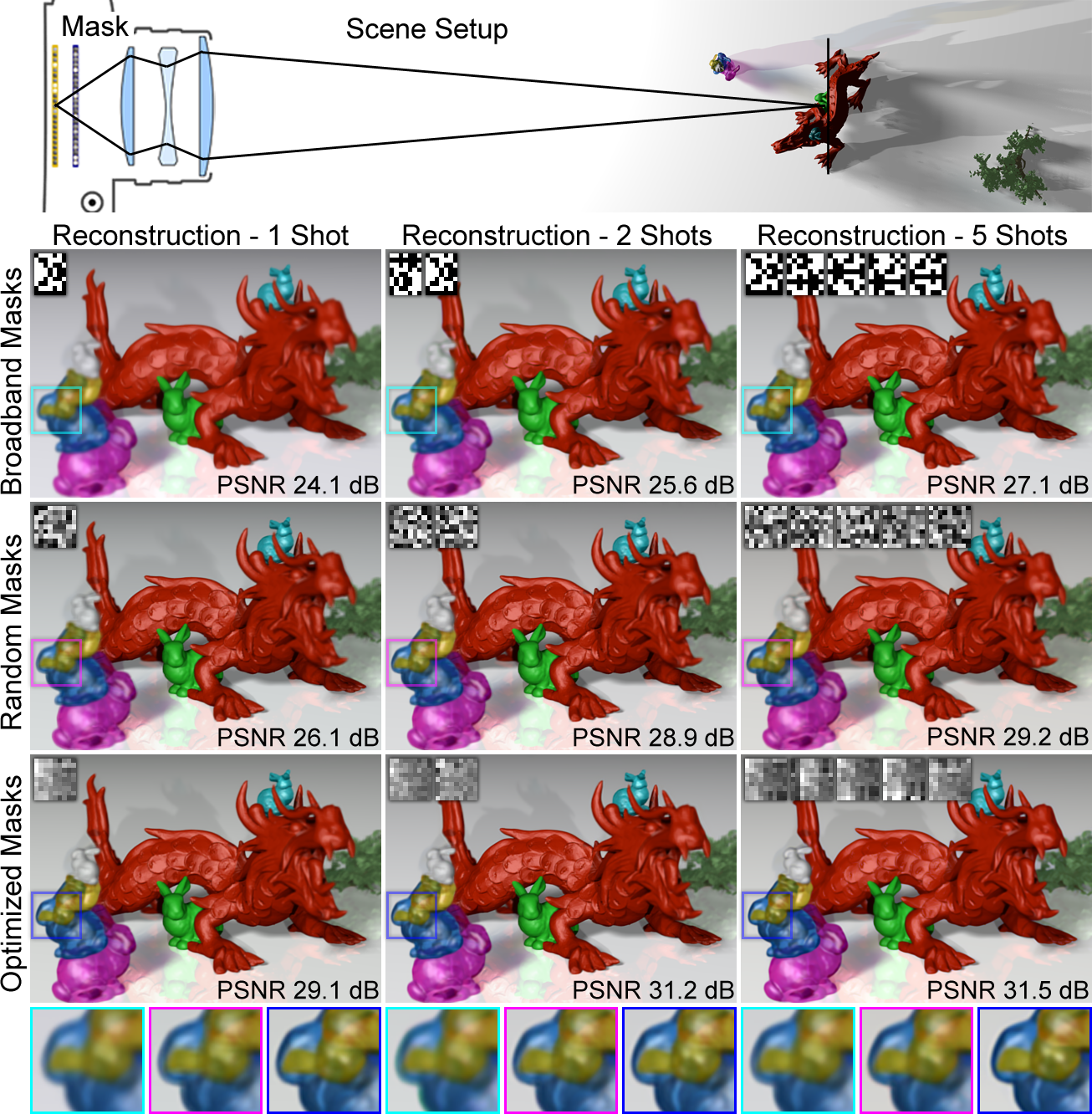
Evaluating optical modulation codes and multiple shot acquisition. We simulate light field reconstructions from coded projections for one, two, and five captured camera images. One tile of the corresponding mask patterns is shown in the insets. For all optical codes, an increasing number of shots increases the number of measurements, hence reconstruction quality. Nevertheless, optimized mask patterns facilitate single-shot reconstructions with a quality that other patterns can only achieve with multiple shots.
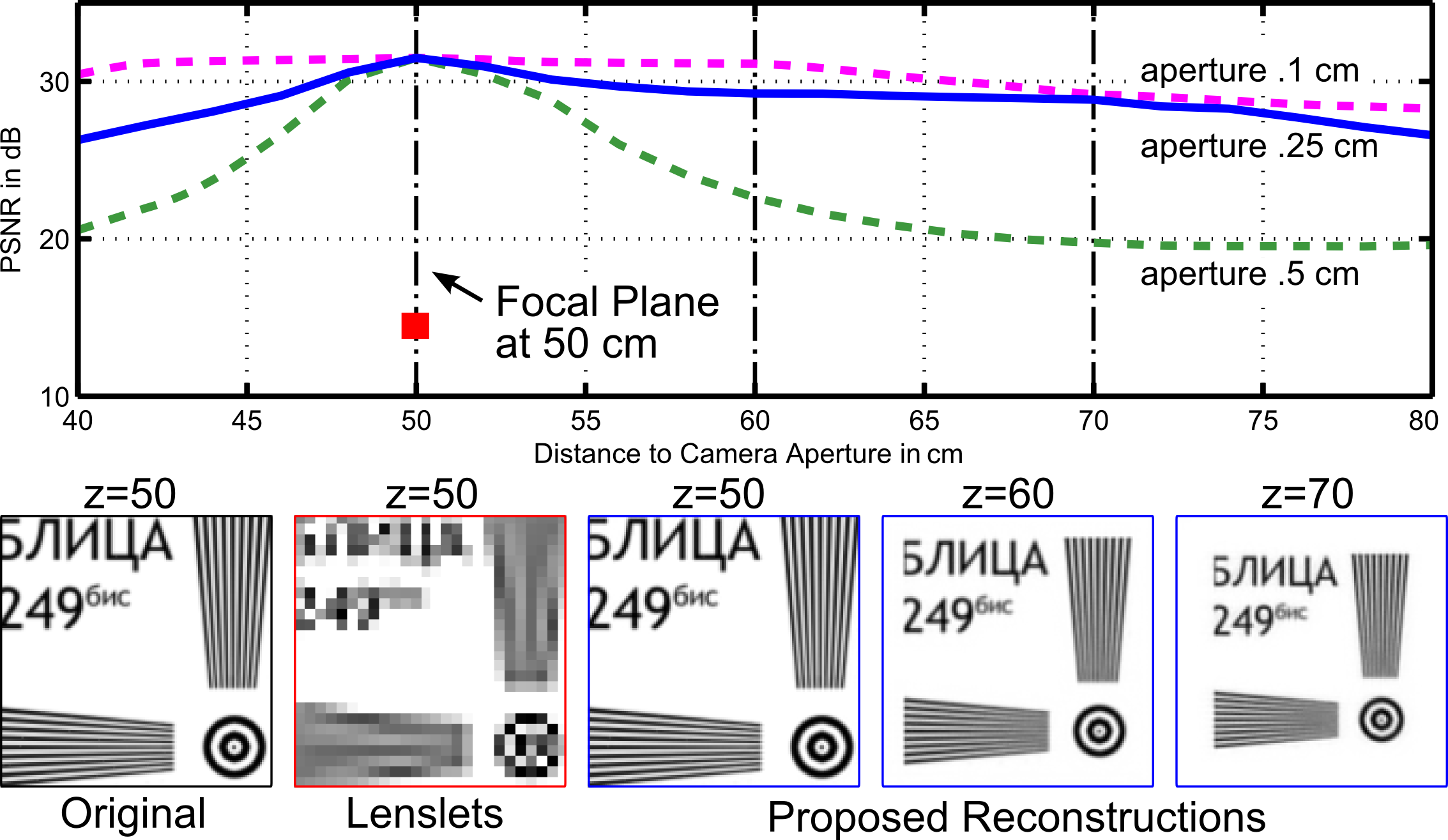
Evaluating depth of field. As opposed to lenslet arrays, the proposed approach preserves most of the image resolution at the focal plane. Reconstruction quality, however, decreases with distance to the focal plane. Central views are shown (on focal plane) for full-resolution light field, lenslet acquisition, and compressive reconstruction; compressive reconstructions are also shown for two other distances. The three plots evaluate reconstruction quality for varying aperture diameters with a dictionary learned from data corresponding to the blue plot (aperture diameter 0.25 cm).
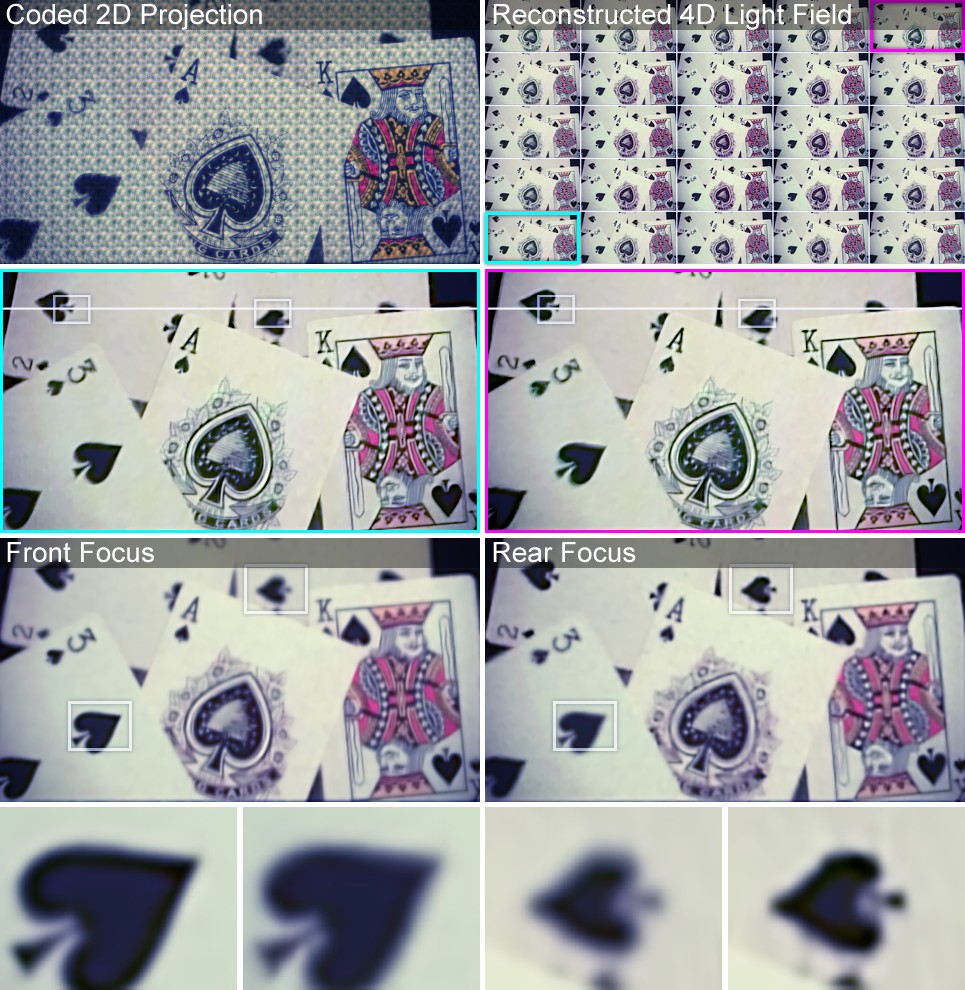
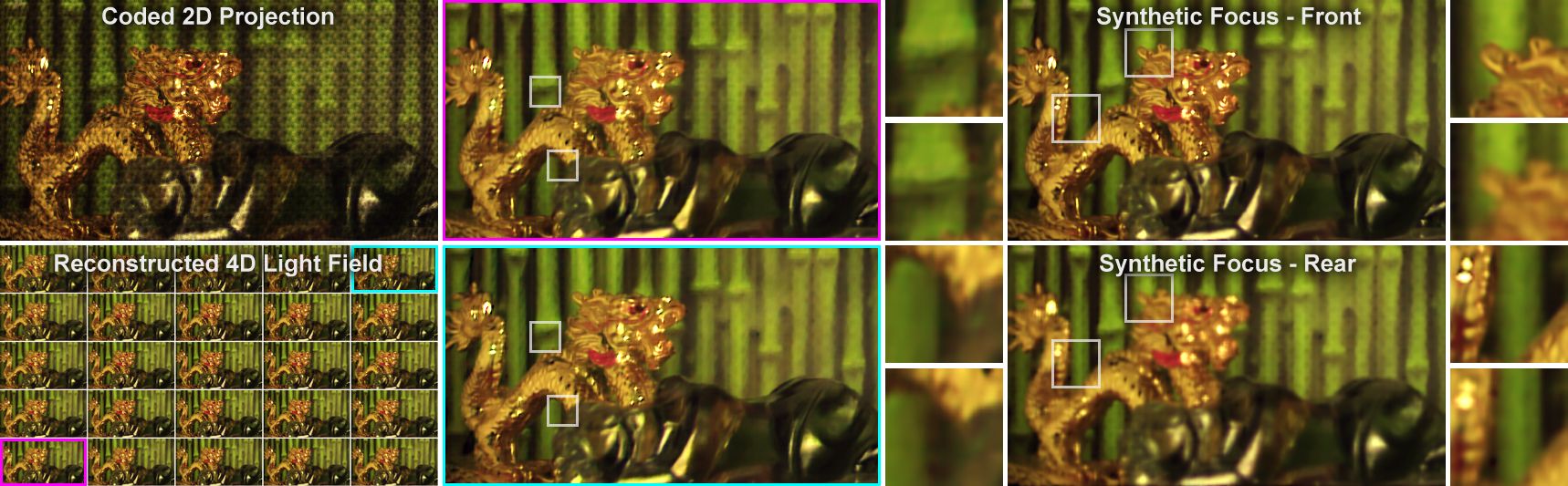
Light field reconstruction from a single coded 2D projection. The scene is composed of diffuse objects at different depths; processing the 4D light field allows for post-capture refocus.

Light field reconstructions of an animated scene. We capture a coded sensor image for multiple frames of a rotating carousel (left) and reconstruct 4D light fields for each of them. The techniques explored in this paper allow for higher-resolution light field acquisition than previous single-shot approaches.

Application: light field compression. A light field is divided into small 4D patches and represented by only few coefficients. Light field atoms achieve a higher image quality than DCT coefficients.

Application: light field denoising. Sparse coding and the proposed 4D dictionaries can remove noise from 4D light fields.