ABSTRACT
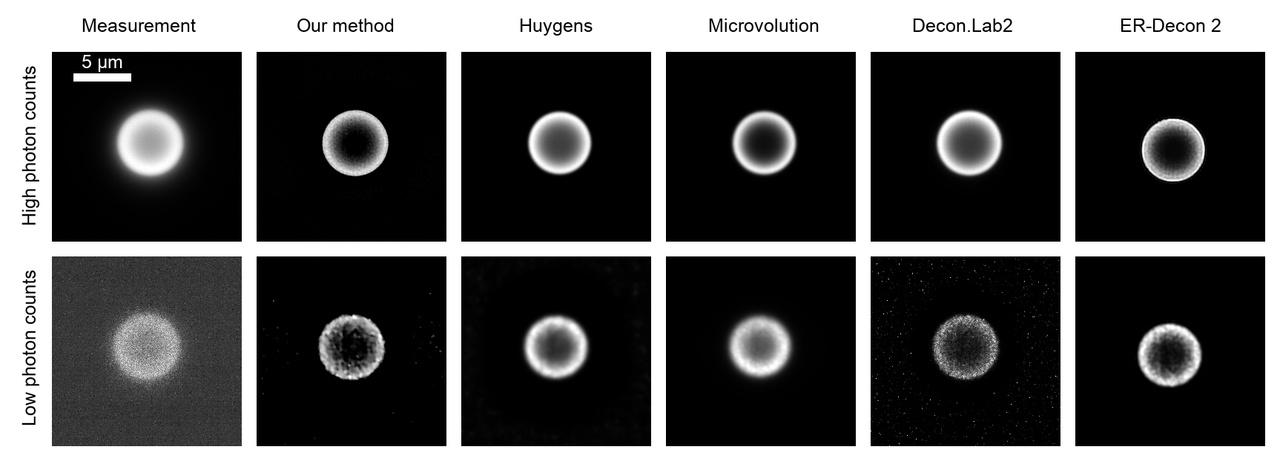
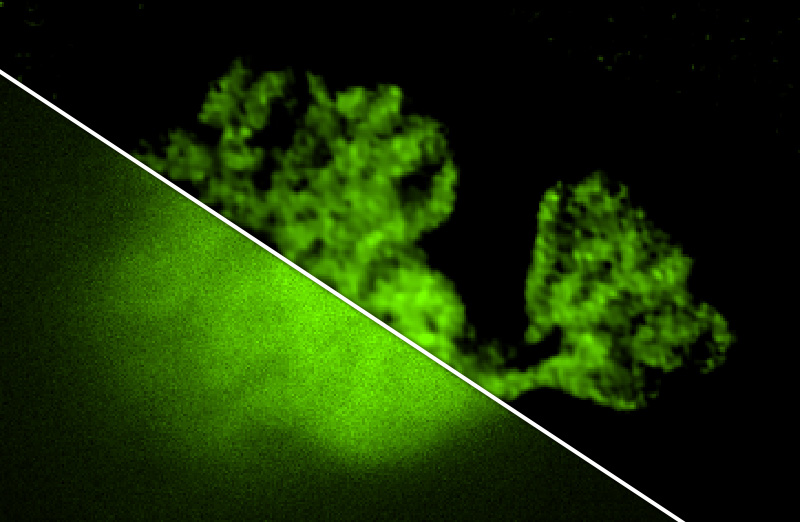
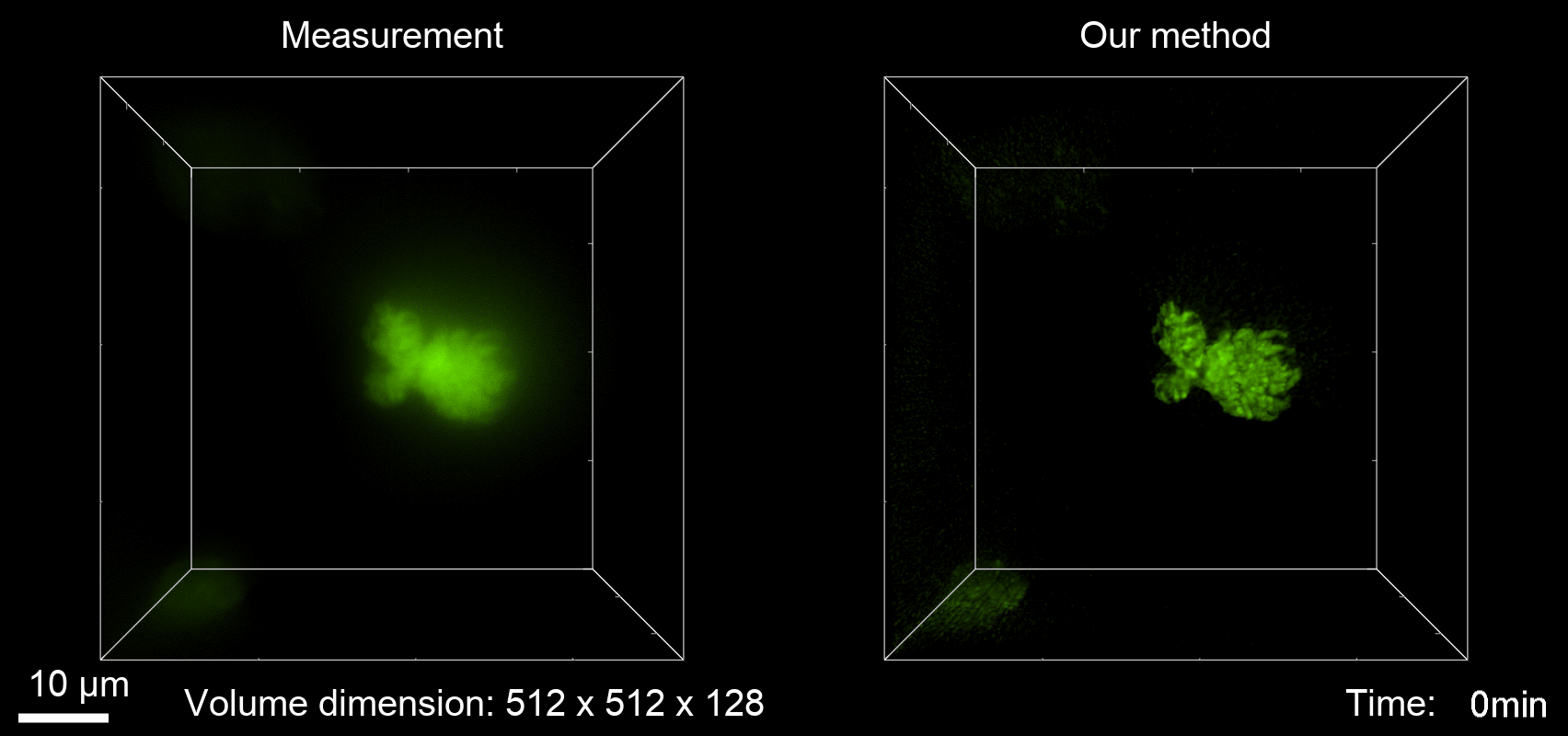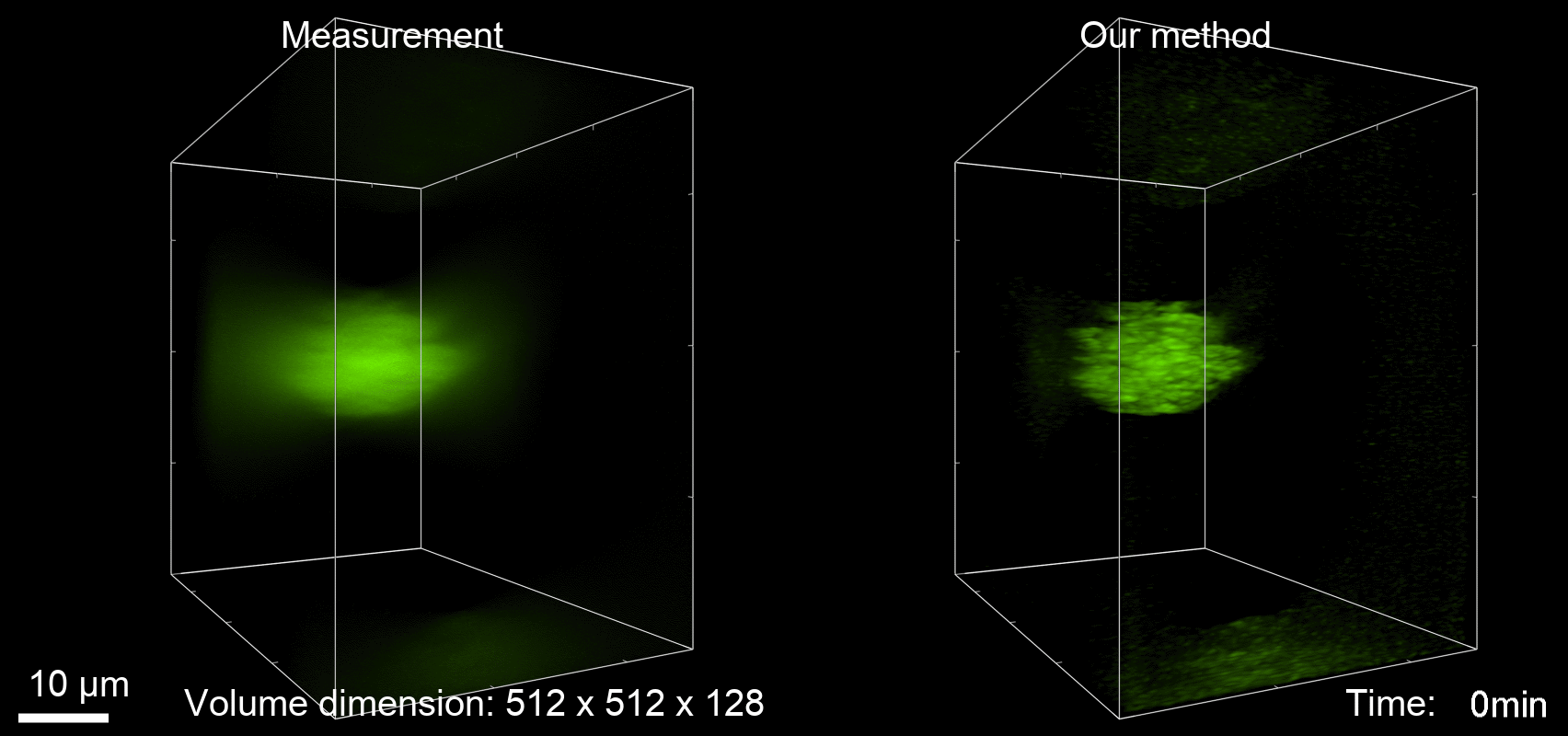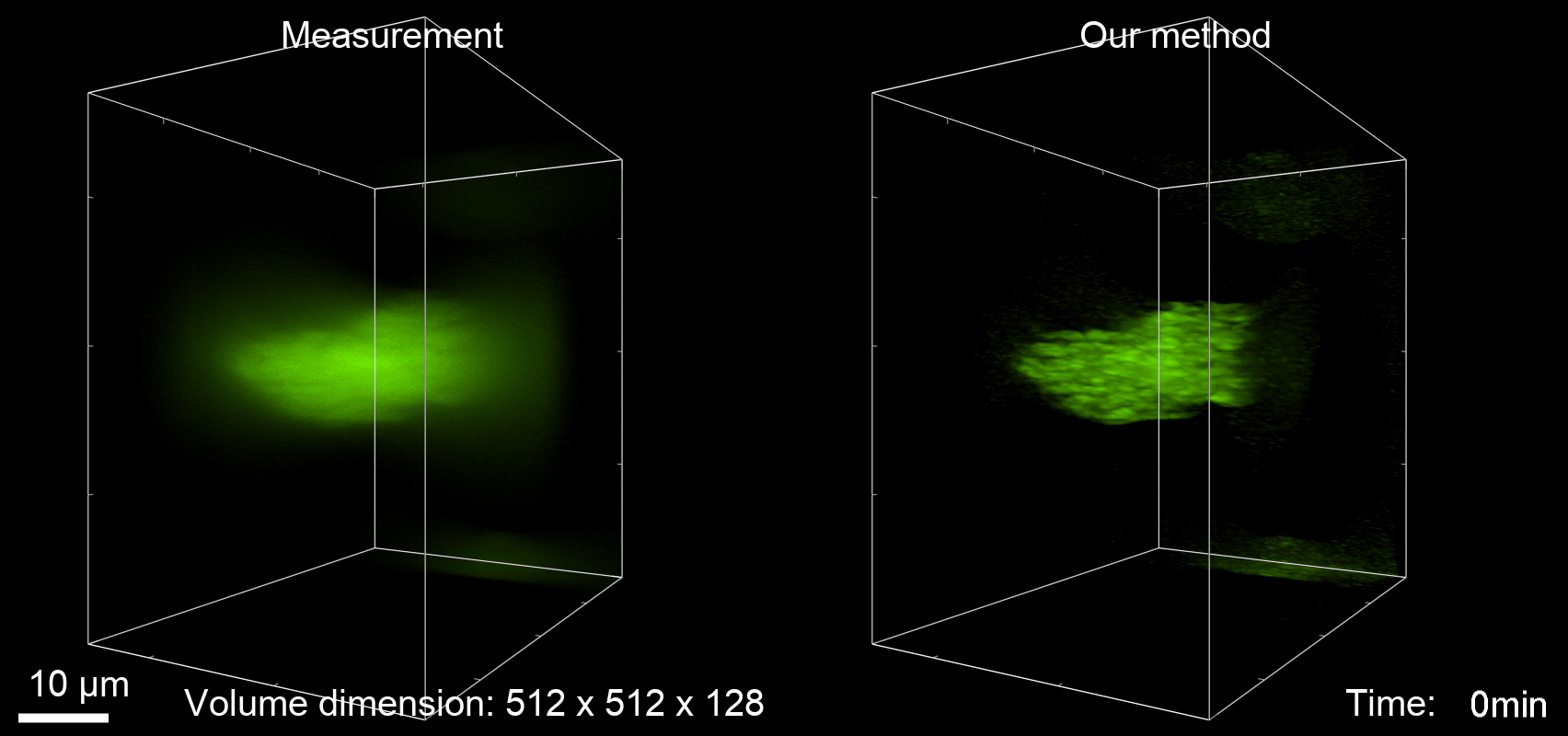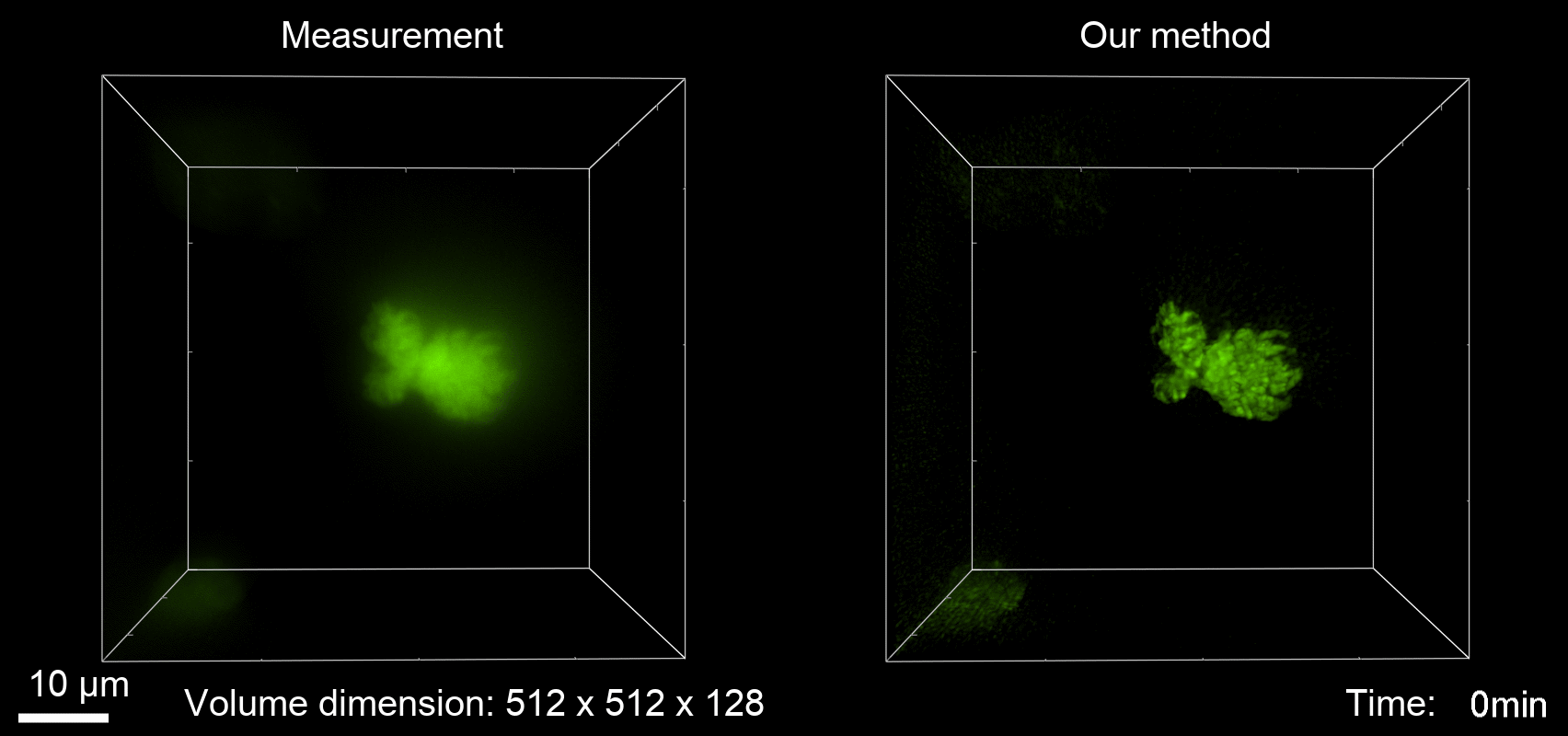
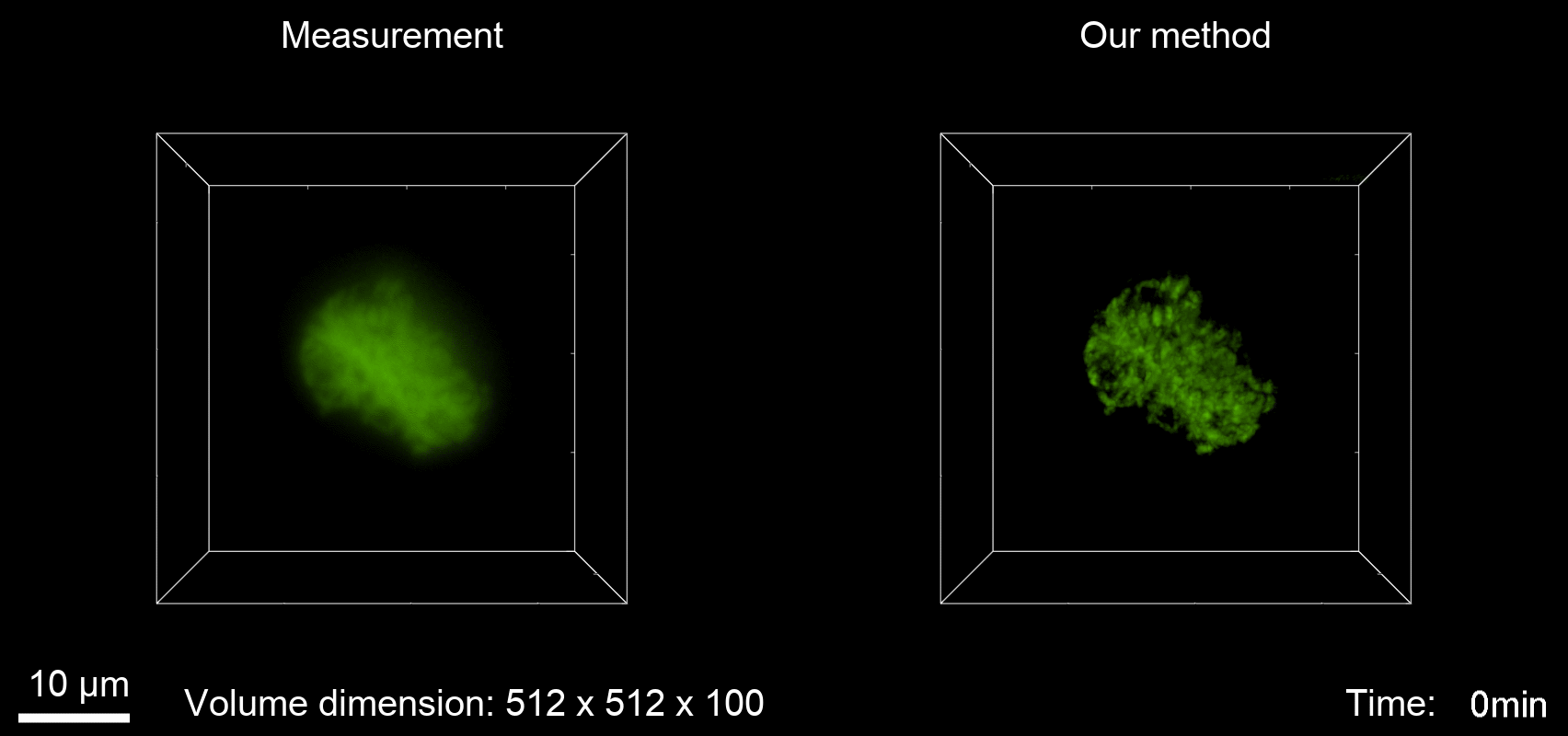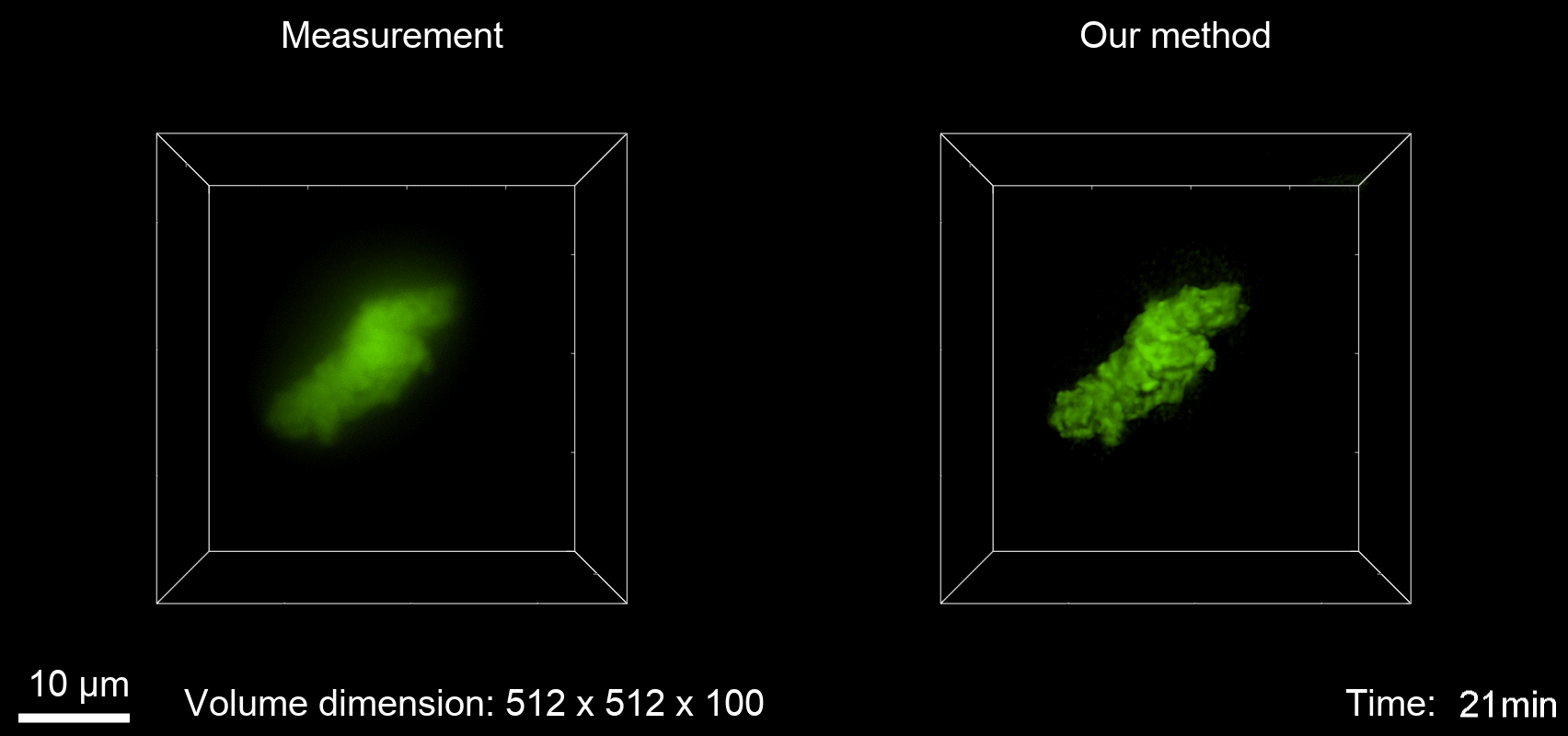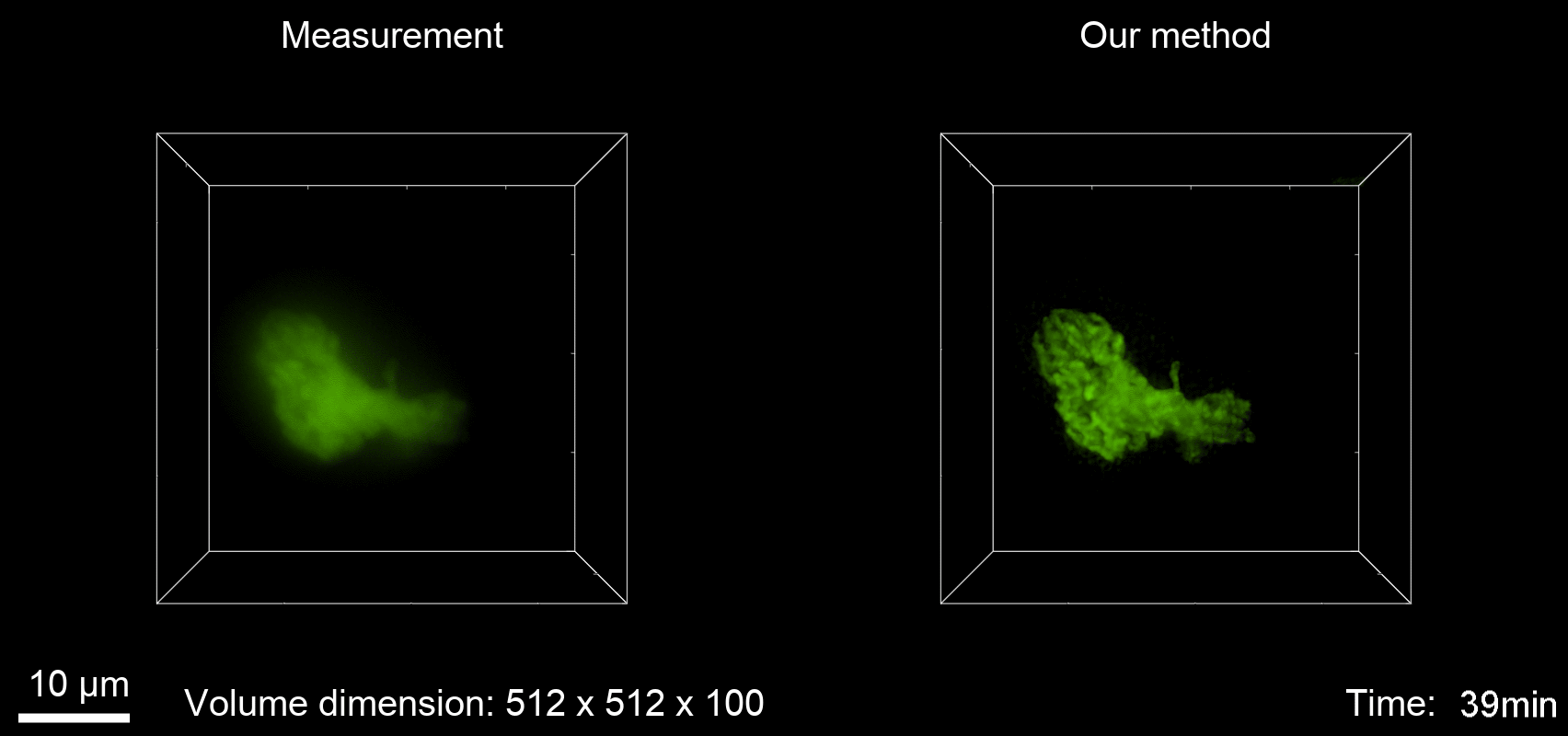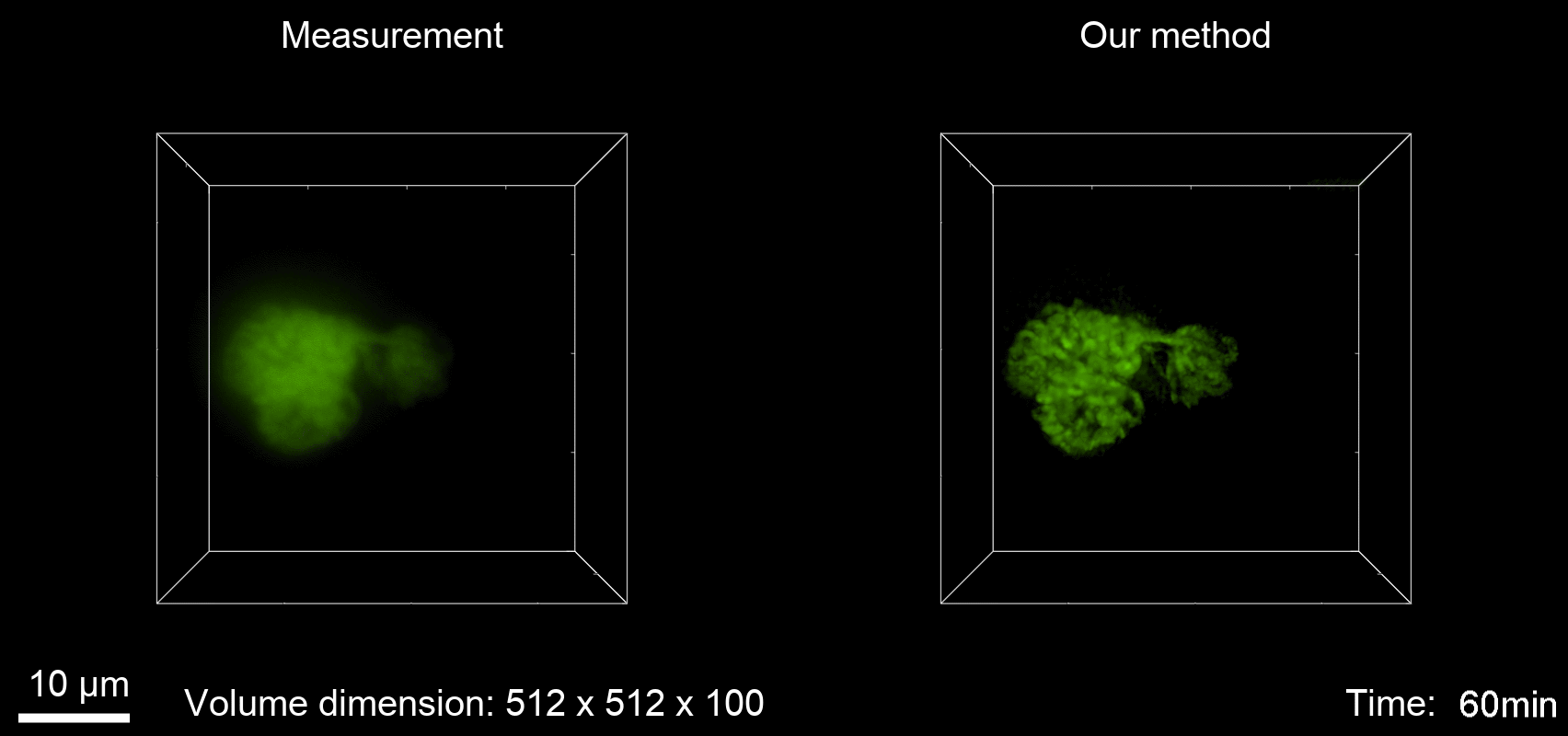
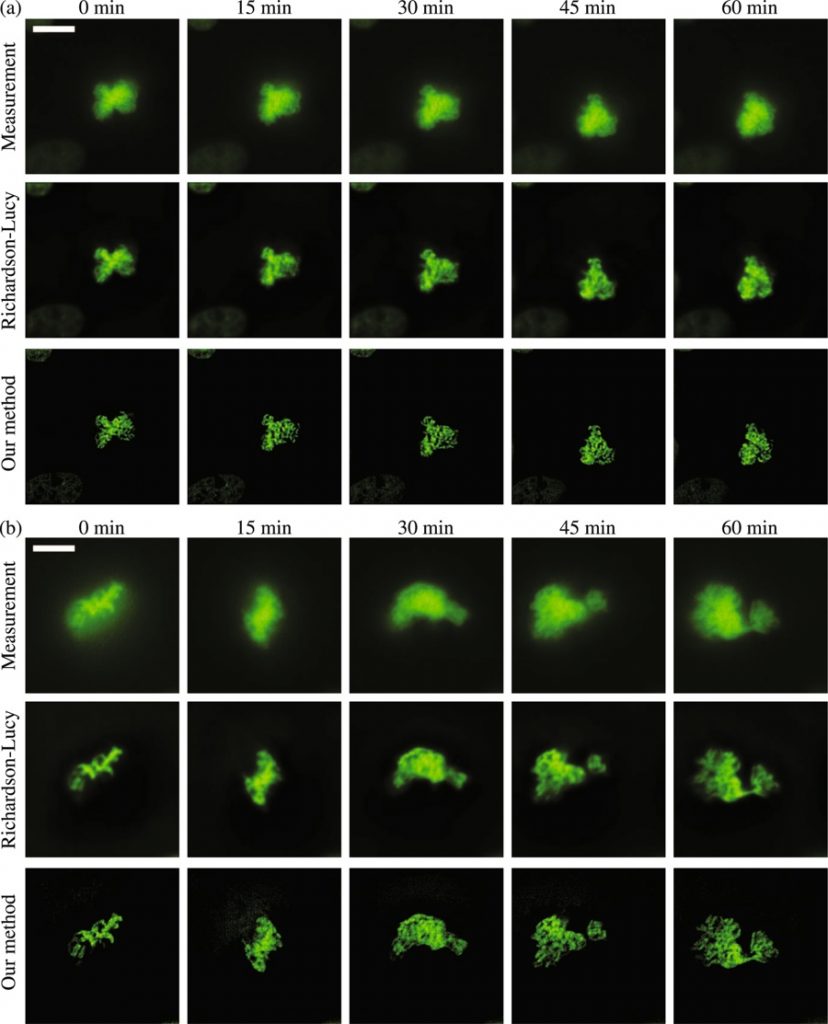
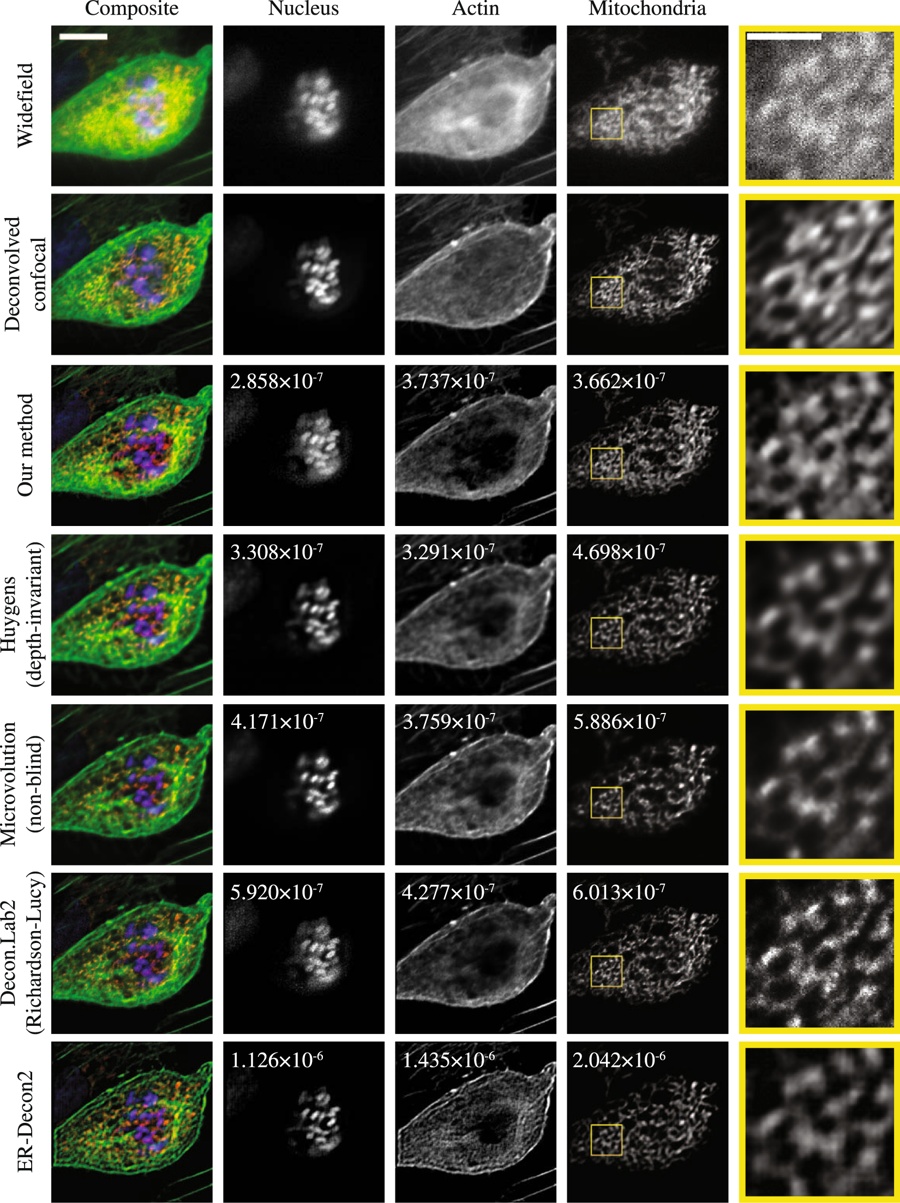
Deconvolution is widely used to improve the contrast and clarity of a 3D focal stack collected using a fluorescence microscope. But despite being extensively studied, deconvolution algorithms can introduce reconstruction artifacts when their underlying noise models or priors are violated, such as when imaging biological specimens at extremely low light levels. In this paper we propose a deconvolution method specifically designed for 3D fluorescence imaging of biological samples in the low-light regime. Our method utilizes a mixed Poisson-Gaussian model of photon shot noise and camera read noise, which are both present in low light imaging. We formulate a convex loss function and solve the resulting optimization problem using the alternating direction method of multipliers algorithm. Among several possible regularization strategies, we show that a Hessian-based regularizer is most effective for describing locally smooth features present in biological specimens. Our algorithm also estimates noise parameters on-the-fly, thereby eliminating a manual calibration step required by most deconvolution software. We demonstrate our algorithm on simulated images and experimentally-captured images with peak intensities of tens of photoelectrons per voxel. We also demonstrate its performance for live cell imaging, showing its applicability as a tool for biological research.